
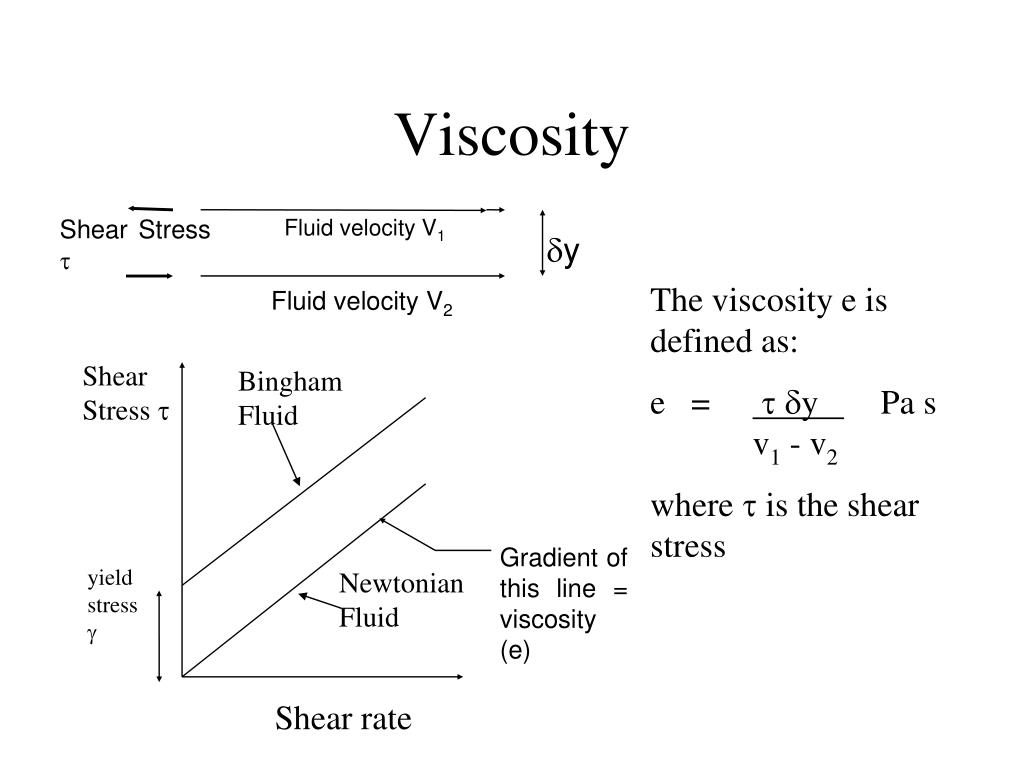
Here, the constant η is known as the coefficient of viscosity, the viscosity, the dynamic viscosity, or the Newtonian viscosity. Isaac Newton postulated that, for straight, parallel and uniform flow, the shear stress, τ, between layers is proportional to the velocity gradient, ∂ u/∂ y, in the direction perpendicular to the layers. In general, in any flow, layers move at different velocities and the fluid's viscosity arises from the shear stress between the layers that ultimately opposes any applied force. Laminar shear, the non-constant gradient, is a result of the geometry the fluid is flowing through (e.g. Volume viscosity is essential for Acoustics in fluids, see Stokes' law (sound attenuation) Newton's theory Extensional viscosity is widely used for characterizing polymers. For example, at "room temperature", water has a nominal viscosity of 1.0 × 10 -3 Pa∙s and motor oil has a nominal apparent viscosity of 250 × 10 -3 Pa∙s. Simply put, this quantity is the ratio between the pressure exerted on the surface of a fluid, in the lateral or horizontal direction, to the change in velocity of the fluid as you move down in the fluid (this is what is referred to as a velocity gradient). That is why they are often referred to as simply viscosity. Shear viscosity and dynamic viscosity are much better known than the others. Extensional viscosity is the viscosity coefficient when the applied stress is an extensional stress (valid for non-Newtonian fluids).Shear viscosity is the viscosity coefficient when the applied stress is a shear stress (valid for non-Newtonian fluids).Bulk viscosity is the same as volume viscosity.Volume viscosity determines the dynamics of a compressible Newtonian fluid.Kinematic viscosity is the dynamic viscosity divided by the density for a Newtonian fluid.Dynamic viscosity determines the dynamics of an incompressible Newtonian fluid.They are introduced in the main books on hydrodynamics and rheology. There are several different viscosity coefficients depending on the nature of applied stress and nature of the fluid. When looking at a value for viscosity, the number that one most often sees is the coefficient of viscosity. A viscous glue was made from mistletoe berries and used for lime-twigs to catch birds. The word "viscosity" derives from the Latin word " viscum" for mistletoe. 5.1.1 Effect of temperature on the viscosity of a gas.4.1.3 Dynamic versus kinematic viscosity.4.1.1 Viscosity (dynamic/absolute viscosity).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
